Optical spectrometers have long been hailed for their ability to analyze light and measure its properties across various segments of the electromagnetic spectrum. However, traditional spectrometer designs have been characterized by their bulkiness and high cost, making them less accessible outside of specialized facilities. As a result, there has been a growing demand for more compact and affordable optical spectrometers that can be deployed on a larger scale.
The Breakthrough
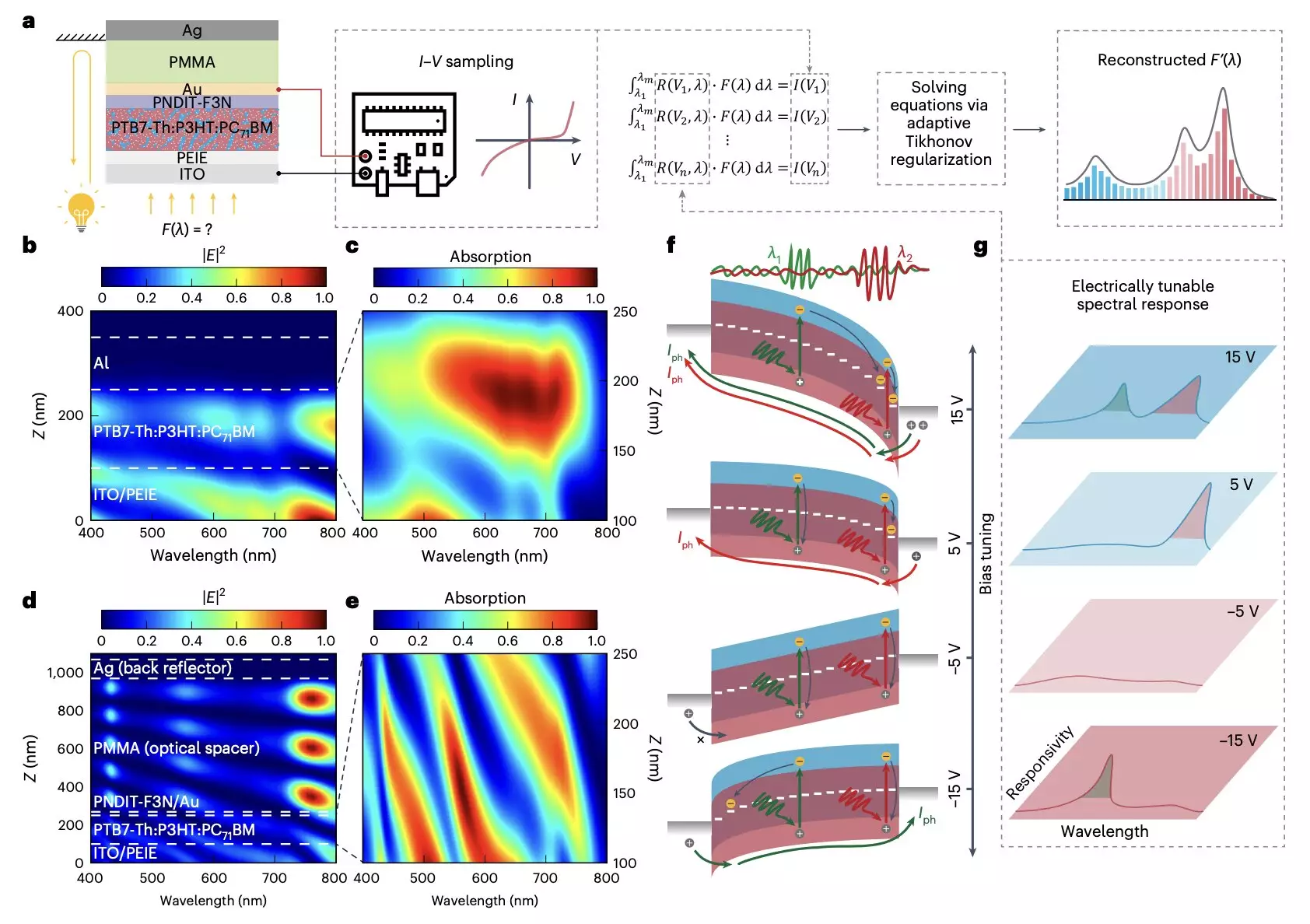
In response to this demand, electronics engineers have been exploring new approaches to develop miniaturized optical spectrometers that are both portable and cost-effective. One recent development in this field is a micro-sized optical spectrometer designed by researchers at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and other institutes in China. This innovative spectrometer, showcased in a paper published in Nature Electronics, is based on an organic photodetector with a bias-tunable spectral response.
The key to the functionality of this new optical spectrometer lies in a novel technique that manipulates the wavelength-dependent location of photocarrier generation in photodiodes. By utilizing a trilayer contact consisting of a transparent back contact, an optical spacer, and a back reflector, the researchers were able to create a photomultiplication-type organic photodetector (PM-OPD) that operates with high efficiency and precision. This cutting-edge design allows for the computational reconstruction of incident light spectra from photocurrents collected at different bias voltages.
The miniaturized optical spectrometer underwent rigorous testing, demonstrating its capability to operate across the entire visible spectrum with a remarkable sub-5-nm resolution. Notably, the researchers were able to leverage this technology to develop an 8 x 8 spectroscopic sensor array for hyperspectral imaging, showcasing the versatility and potential applications of this innovative approach.
The successful development of this micro-sized optical spectrometer opens up exciting possibilities for the future of spectroscopy. With the potential for even further miniaturization and cost reduction, this technology could pave the way for the creation of new cutting-edge devices that have the power to revolutionize research and medical practices. By inspiring the development of similar micro-sized optical spectrometers, this breakthrough has the potential to drive innovation in a wide range of fields.

Leave a Reply