Recent advancements in quantum physics have unveiled a profound and elegant relationship between energy and information transmission across interfaces of quantum field theories. A dedicated cohort of researchers, including prominent figures like Hirosi Ooguri and Fred Kavli, have published findings in the esteemed journal Physical Review Letters that could reshape our understanding of fundamental physics principles. This work not only simplifies a previously complex domain but also lays the groundwork for further exploration and innovation in theories of quantum mechanics.
The Challenge of Quantum Calculations
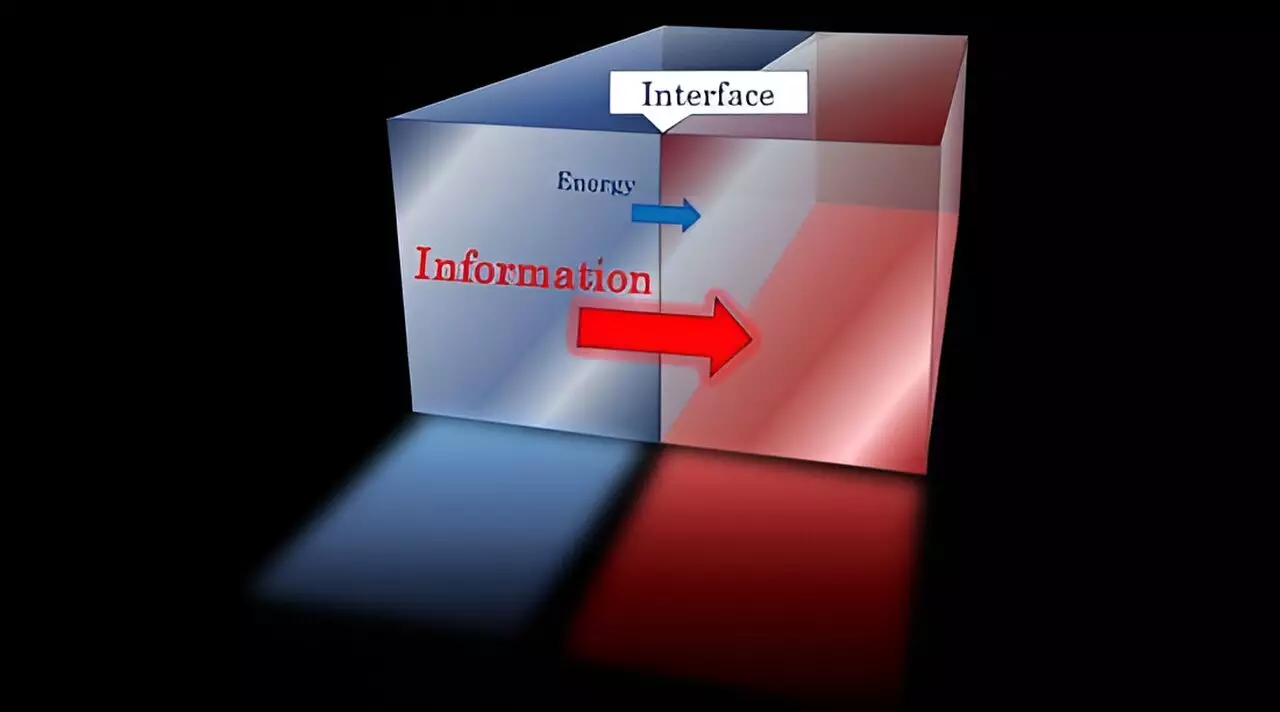
Quantum physics, especially concerning the interactions at various interfaces between different theories, is notoriously difficult to parse. Traditional methods for calculating rates of energy and information transfer have often resulted in convoluted equations that eclipse any intuitive understanding of their relationships. The revelation by this international team shows that instead of a labyrinthine approach, a straightforward comparative analysis yields compelling insights. The established inequalities unveil a structured hierarchy among energy transfer rates, information transfer rates, and the expansive nature of Hilbert space.
The Significance of Scale Invariance
At the heart of their findings lies the significance of scale invariance in two-dimensional quantum field theories. This crucial concept allows researchers to unify seemingly disparate elements of quantum mechanics, thereby making it easier to see the correlations between energy and information. The implications here are far-reaching; not only do they clarify theoretical frameworks, but they also provoke deeper questions regarding how we interact with and comprehend the fundamental aspects of the universe.
New Inequalities: A Scientific Breakthrough
The researchers established an elegant inequality: energy transmittance must always be lesser than or equal to information transmittance, which in turn must be less than or equal to the size of Hilbert space. This means that for energy to be transmitted, a corresponding stream of information must also flow, underscoring a reliance on a sufficient number of quantum states. The groundbreaking aspect of this discovery lies in the assertion that stronger inequalities are unattainable, solidifying the foundational nature of these relationships in quantum theory.
Implications for Future Research
These findings pave the way for extensive future research and may influence multiple areas within theoretical and particle physics. As institutions and academics dive deeper into the implications of this hierarchy, one can expect a ripple effect across quantum field research, computational methods, and even applications in quantum computing. Understanding the intrinsic connections between energy and information may also refine our approach to complex systems, fostering new technological advancements and enriching our grasp of physical laws.
This fresh perspective on quantum interfaces signifies an exciting juncture in the scientific community, inviting enthusiasts and professionals alike to reassess notions about energy and information—two pillars of our understanding of the universe. The simplicity and universality of these relationships offer not only clarity in theory but also a beacon of potential innovation in realistic applications.

Leave a Reply