Metal halide perovskites have garnered attention in recent years due to their remarkable optoelectronic properties, making them attractive candidates for thin-film transistor development. Specifically, tin (Sn) halide perovskites have demonstrated impressive field-effect hole mobilities exceeding 70 cm2 V−1 s−1 in p-type transistors. However, the lack of similar performance in n-type transistors poses a challenge for the development of complementary logic circuits. Lead halide perovskites have been explored as potential candidates for n-type transistors but suffer from ionic defects that limit electron mobilities to 3–4 cm2 V−1 s−1.
Researchers from various institutions have introduced a new approach to enhance the performance of n-type transistors based on metal halide perovskites. By utilizing formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3) perovskite and incorporating a methylammonium chloride (MACI) additive, they have achieved field-effect mobilities of up to 33 cm2 V−1 s−1 in n-type transistors. This breakthrough paves the way for the development of high-performance integrated circuits containing metal halide perovskite transistors.
The addition of the MACI additive played a crucial role in enhancing the performance of the n-type transistors. It facilitated the regulation of strain in FAPbI3, improved material properties, and stabilized the perovskite lattice structure. This approach resulted in superior surface morphology, crystallinity, and orientation, essential for optimizing transistor performance.
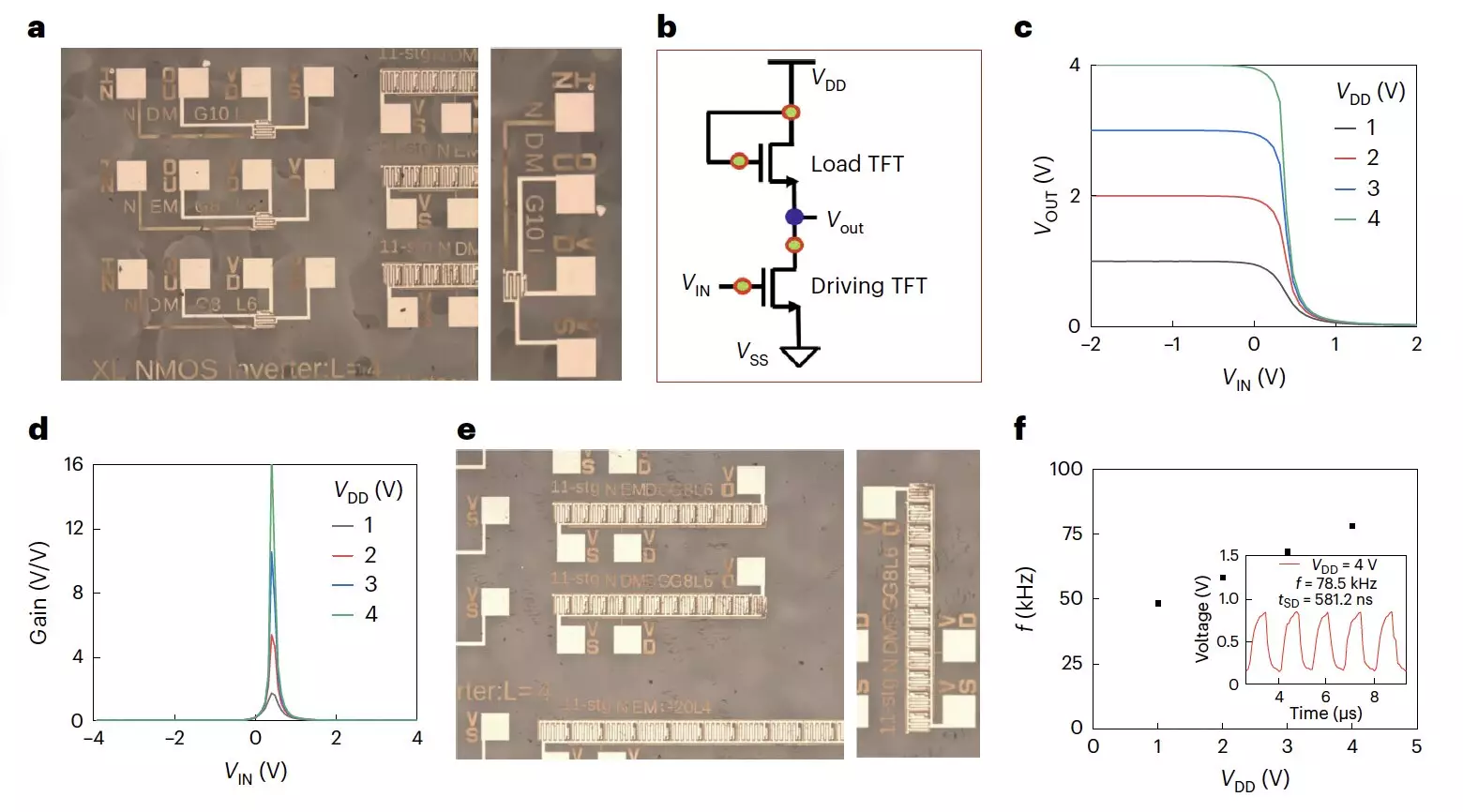
Initial tests on the n-type transistors demonstrated promising results, including high electron mobilities, minimal hysteresis, and excellent operational stability under both negative and positive bias stress. The researchers were able to fabricate all-perovskite unipolar inverters and 11-stage ring oscillators using their transistors. This suggests that the proposed fabrication strategy could lead to the development of cost-effective integrated circuits with superior performance.
With the successful demonstration of high-performing n-type transistors based on metal halide perovskites, further research and integration into various electronic devices are imminent. The potential applications of these transistors extend beyond inverters and oscillators, opening new avenues for the design of advanced electronic components. The continued refinement of fabrication techniques and materials could revolutionize the field of thin-film transistor technology.
The development of metal halide perovskite-based thin-film transistors represents a significant advancement in the realm of semiconductor devices. By addressing the limitations of traditional materials and exploring innovative strategies, researchers have unlocked new possibilities for high-performance electronics. The integration of n-type transistors with superior properties offers a glimpse into the future of efficient and cost-effective integrated circuits.

Leave a Reply